Ayahuasca Powder
$80.00 – $350.00Price range: $80.00 through $350.00
Modern yopo snuff, consisting of Anadenanthera peregrina seeds toasted, ground into powder, and mixed with 1/3 baking soda.
Ayahuasca Powder: An Overview
Ayahuasca powder is a traditional psychoactive brew originating from the Amazon rainforest, used for centuries by indigenous tribes for spiritual, medicinal, and ritualistic purposes. In recent years, it has gained popularity worldwide for its profound effects on consciousness, healing, and self-awareness.
What is Ayahuasca Powder?
Ayahuasca powder is the dry, ground form of the psychedelic brew made from the Banisteriopsis caapi vine and the leaves of the Psychotria viridis shrub or other DMT-containing plants. The powder typically contains these dried plant materials, which can be reconstituted into a brew or taken in capsule form.
Components & Preparation:
– Banisteriopsis caapi: Contains MAO inhibitors (harmala alkaloids) that activate the psychoactive compounds.
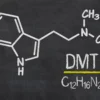
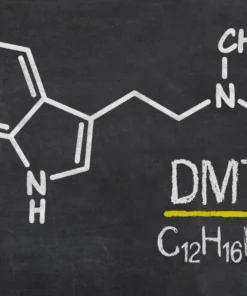
– Psychotria viridis or other DMT plants: Provide DMT (Dimethyltryptamine), a powerful hallucinogen.
– The traditional preparation involves boiling and fermenting these plants into a brew, then drying it into powder form for easier storage and dosage.
Uses & Cultural Significance: Ayahuasca Powder
In traditional Amazonian cultures, ayahuasca is used by shamans and spiritual practitioners to:
– Facilitate communication with spirits
– Diagnose and treat illnesses
– Promote personal growth and insight
– Connect with the natural world
Effects & Experience:
When consumed, ayahuasca can induce intense visual and auditory hallucinations, emotional releases, and deep introspection. The experience often lasts 4-6 hours and can be both challenging and transformative. Ayahuasca Powder
Legal & Safety Considerations:
While ayahuasca is considered a sacred medicine in indigenous communities, its legal status varies globally. In some countries, it is classified as a controlled substance, while in others, religious exemptions exist. Due to its potent effects, it should only be used under the guidance of experienced facilitators and in safe, supportive settings.
Potential Benefits & Risks:
– Benefits: Emotional healing, trauma processing, spiritual awakening, increased self-awareness. Ayahuasca Powder
– Risks: Psychological distress, adverse reactions, interactions with medications, or underlying health conditions.
Conclusion:
Ayahuasca powder holds a rich cultural history and offers profound potential for personal and spiritual development. However, due to its potency, respect, caution, and proper guidance are essential for those seeking to explore its depths.
A hallucinogenic snuff, or psychedelic snuff, is a powder prepared from plants containing psychedelic alkaloids and insufflated (snorted) to produce hallucinogenic effects.[1][2][3] Hallucinogenic snuffs have been used as entheogens by indigenous peoples of South and Central America for thousands of years.[1][2][3] The snuffs are prepared most commonly from Anadenanthera species including Anadenanthera peregrina and Anadenanthera colubrina, but also from species of other genuses including Mimosa and Virola.[1][2][4] Ayahuasca Powder
They have local names including cohoba, ebene, paricá, yopo, cébil, and vilca, among many others.[1][2][3] The active compounds in these snuffs include the serotonergic psychedelics bufotenin (5-HO-DMT), dimethyltryptamine (DMT), and 5-MeO-DMT.[1][2][3] The materials of snuffs may also be used as enemas instead of via insufflation.[1][5]
Although previously thought to be non-hallucinogenic and/or toxic, ethnobotanist Jonathan Ott and colleagues showed in 2001 that bufotenin is an active psychedelic similarly to DMT and 5-MeO-DMT and does not necessarily produce major adverse effects.[6][7] Bufotenin is the only significant alkaloid present in the seeds of Anadenanthera species, from which many snuffs are prepared, with percentages of 2.7–12.4% bufotenin relative to 0.04–0.16% for 5-MeO-DMT and Ayahuasca Powder.[6][7]
According to journalist Hamilton Morris, who has also self-experimented with bufotenin, the effects of pure bufotenin are like a cross between those of DMT and 5-MeO-DMT, though unlike the others it tends to be accompanied by severe nausea and vomiting.[8][9] Morris has stated that, due to its use in the form of hallucinogenic snuffs, bufotenin may be the psychedelic with the longest known history of human entheogenic use.[8][9] However, although bufotenin may be active as a hallucinogen, it can produce powerful and potentially dangerous cardiovascular side effects along with its emetic effects.[10]
| Quantity | 200 g, 500g, 1kg |
|---|
Be the first to review “Ayahuasca Powder” Cancel reply
Related products
Dmt











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.