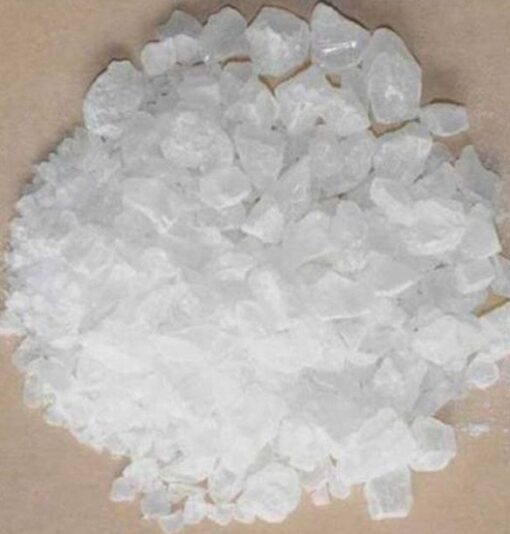
DMT Crystals
$55.00 – $499.00Price range: $55.00 through $499.00
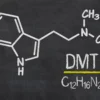
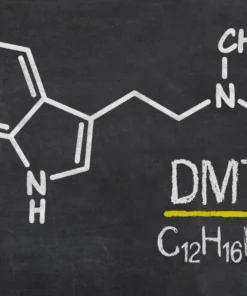
| Formula | C12H16N2 |
|---|---|
| Molar mass | 188.274 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.099 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 40 °C (104 °F) |
DMT Crystals
Introduction:
DMT, or N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, is a powerful naturally occurring psychedelic substance known for its intense and profound hallucinogenic effects. It is often found in crystalline form, known as DMT crystals, which are typically white or off-white and can be vaporized, smoked, or ingested for their psychoactive properties.
What Are DMT Crystals?
DMT crystals are the pure, crystalline form of the compound. They are usually synthesized in laboratories or extracted from certain plants like *Mimosa hostilis* or *Acacia* species, which naturally contain DMT. The crystals are prized for their potency and purity, making them a sought-after substance in psychedelic communities.
Physical Characteristics:
– Appearance: Usually white or off-white crystalline powder or chunks.
– Texture: Hard or brittle, can be ground into a fine powder.
– Solubility: DMT is soluble in alcohol and other organic solvents, which is useful during extraction or purification processes.
Methods of Use:
– Vaporization: DMT crystals are often vaporized using specialized devices called vaporizers or smoked in a glass pipe.
– Extraction: The process involves isolating DMT from plant material through chemical extraction techniques.
– Oral Ingestion: In some cases, DMT is ingested in combination with MAOIs (as in Ayahuasca), which allows for a longer-lasting experience.
Effects and Experience:
When vaporized or smoked, DMT produces a rapid onset of effects, often within minutes, with a duration of about 15-30 minutes. Users report:
– Intense visual and auditory hallucinations
– Encounters with otherworldly beings or entities
– A sense of transcendence or spiritual awakening
– Altered perception of time and self-awareness
Legal Status and Safety:
DMT is classified as a Schedule I substance in many countries, making its possession and use illegal outside of approved research or traditional contexts like Amazonian shamanic practices. Due to its potency, DMT can cause intense psychological experiences, so safety precautions and awareness are essential.
Cultural and Spiritual Significance:
Historically, DMT-containing plants have been used in indigenous rituals for spiritual and healing purposes. In modern times, many seek DMT crystals for personal spiritual exploration or to gain insights into consciousness.
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), also known as N,N-dimethyltryptamine (N,N-DMT) and DiMiTri is a serotonergic hallucinogen and investigational drug of the tryptamine family that occurs naturally in many plants and animals.[1][2][3][9] DMT is used as a psychedelic drug and prepared by various cultures for ritual purposes as an entheogen.[10]
DMT has a rapid onset, intense effects, and a relatively short duration of action. For those reasons, DMT was known as the “businessman’s trip” during the 1960s in the United States, as a user could access the full depth of a psychedelic experience in considerably less time than with other substances such as LSD or psilocybin mushrooms.[11] DMT can be inhaled or injected and its effects depend on the dose, as well as the mode of administration. When inhaled or injected, the effects last about five to fifteen minutes. Effects can last three hours or more when orally ingested along with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), such as the ayahuasca brew of many native Amazonian tribes.[12] DMT induces intense, often indescribable subjective experiences involving vivid visual hallucinations, altered sensory perception, ego dissolution, and encounters with seemingly autonomous entities. DMT is generally considered non-addictive with low dependence and no tolerance buildup, but it may cause acute psychological distress or cardiovascular effects, especially in predisposed individuals.
DMT was first synthesized in 1931. It is a functional analog and structural analog of other psychedelic tryptamines such as O-acetylpsilocin (4-AcO-DMT),[13] psilocybin (4-PO-DMT), psilocin (4-HO-DMT), NB-DMT, O-methylbufotenin (5-MeO-DMT), and bufotenin (5-HO-DMT). Parts of the structure of DMT occur within some important biomolecules like serotonin and melatonin, making them structural analogs of DMT.
| Quantity | 1g, 5g, 10g |
|---|
Be the first to review “DMT Crystals” Cancel reply
Related products
Dmt











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.